In thermoplastic elastomers, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a subcategory. Usually, these materials are block copolymers of polyether or polyester with classical polyurethane.
In the polymerization process, different material properties are usually adjusted by combining different raw materials. In rare cases, subsequent compounding with various additives is also carried out.
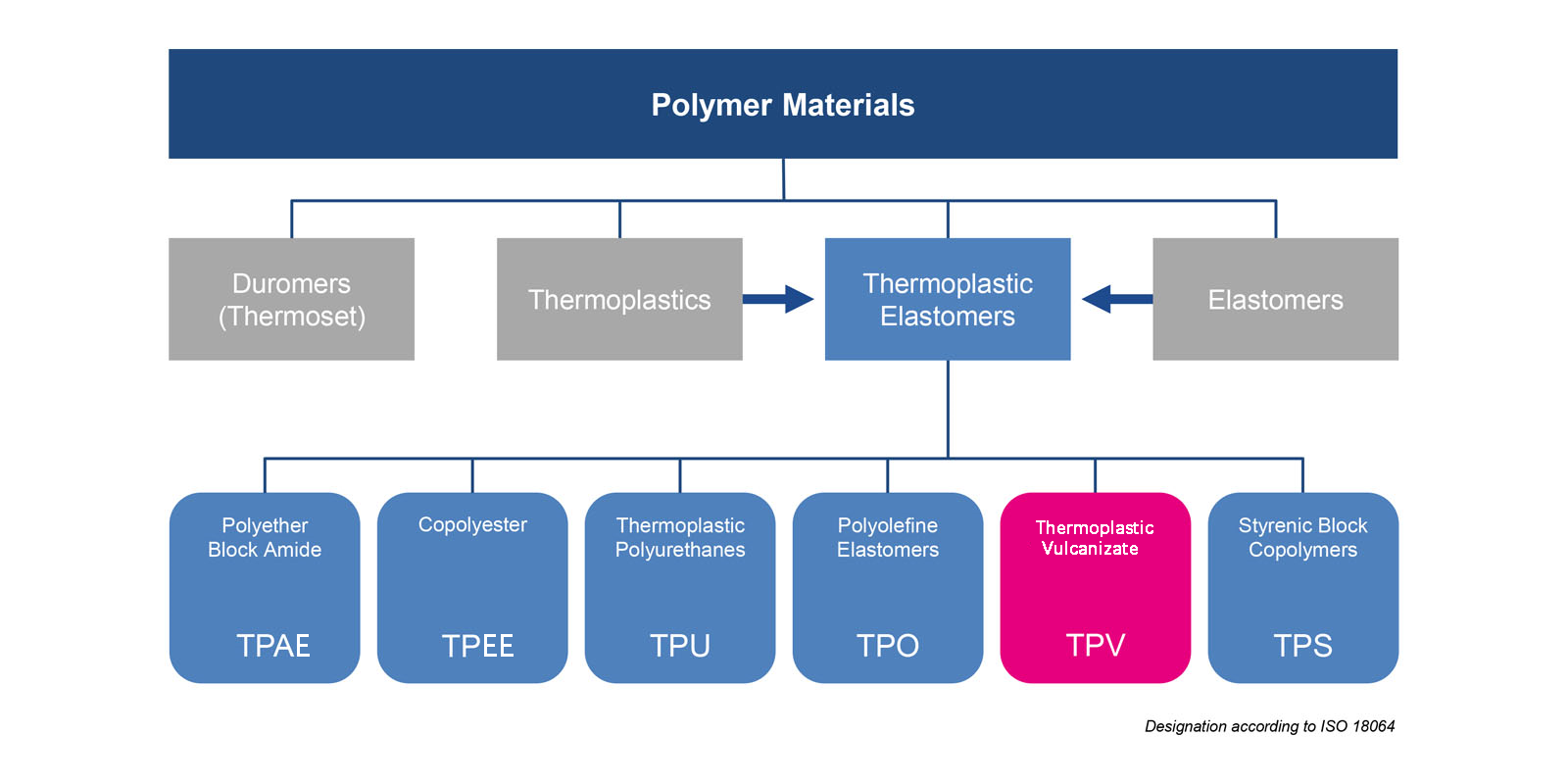
Thermoplastic elastomers are produced in particle form and delivered to customers. There are various methods for processing particles. The most commonly used methods include injection molding and extrusion processes. However, thermoplastic elastomers can also be blown or processed using 3D printing.
The main characteristics of TPU materials are their high mechanical strength and excellent wear resistance.
TPU plastics exhibit good resistance to various non-polar chemicals. On the contrary, materials have a certain sensitivity to degradation in contact with water and aqueous solutions, especially at high temperatures. Therefore, in order to avoid material damage, it is necessary to dry the TPU compound before processing. This also supports the machinability of the material.
Depending on the manufacturer, TPU is also produced for the consumer market. The material can be colored, and some manufacturers also offer semi transparent TPU.
·Wear resistance
·Mechanical strength
·Low temperature flexibility
·Heat aging
·Tolerance to various non-polar chemicals
·Injectability
The hardness level of thermoplastic polyurethane is usually between 60 Shore A and 80 Shore D. Compared to typical TPS products, TPU materials are significantly harder and rarely compete directly with each other.
Sungalon TPE itself does not produce TPU and does not sell these plastics. However, various TPUs are used as performance modifiers and modifiers for styrene based thermoplastic elastomers of Sungalon TPE.